Abstract:
This project presents the design and implementation of a hydraulic braking system using syringes, aimed at providing a hands-on learning experience for mechanical engineering students. The system simulates the functionality of traditional hydraulic braking systems, offering insights into fluid dynamics and pressure transmission principles.
Introduction:
The hydraulic braking system using syringes project seeks to enhance the understanding of hydraulic systems among mechanical engineering students. By employing simple and accessible materials such as syringes, tubing, and brake calipers, the project aims to demonstrate fundamental concepts of fluid dynamics and pressure transmission in a practical manner. Through this project, students can gain insights into the design, operation, and performance of hydraulic braking systems, preparing them for future engineering challenges.
Working:
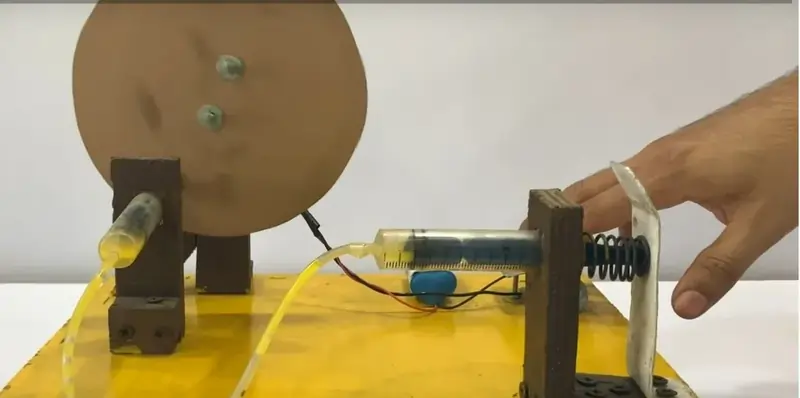
The hydraulic braking system utilizes syringes as hydraulic cylinders, with tubing connecting them to brake calipers. When the brake pedal is pressed, fluid (water or hydraulic fluid) is forced from the syringe through the tubing into the brake calipers, applying pressure to the brake pads and causing them to clamp onto the rotor or wheel. This simulates the braking action, demonstrating the principles of hydraulic pressure transmission and mechanical force conversion.
Applications:
1.Education: Provides a hands-on learning experience for mechanical engineering students to understand hydraulic systems.
2.Training: Useful for training purposes in automotive and mechanical workshops to demonstrate braking system principles.
3.Research: Offers a platform for conducting experiments and research in fluid dynamics and pressure transmission.
Advantages:
1.Accessibility: Utilizes readily available materials such as syringes, tubing, and brake calipers.
2.Affordability: Cost-effective compared to traditional hydraulic braking system components.
3.Demonstration: Clearly illustrates fundamental principles of hydraulic systems in a practical manner.
4.Safety: Provides a safe environment for students to learn about braking system operation without the risks associated with real vehicles.
Conclusion:
The hydraulic braking system using syringes project offers a valuable educational tool for mechanical engineering students to gain practical insights into hydraulic systems. By simulating the functionality of traditional hydraulic braking systems using simple materials, the project enhances understanding and promotes hands-on learning. Furthermore, the project's affordability, accessibility, and safety make it a versatile tool for educational institutions, workshops, and research laboratories. Overall, the project contributes to the advancement of engineering education and facilitates learning in fluid dynamics and pressure transmission principles.